Stomatitis is the name given to lesions of the oral cavity (its mucous membrane), which often manifests itself in the form of spots or sores. Why such a disease can develop in a child, what is stomatitis and how should parents react to its appearance?
Symptoms and signs
It is possible to identify stomatitis in a child by a characteristic clinical picture.
In infants (children under 1 year old)
- A whitish coating on the oral mucosa is typical of fungal stomatitis.
- On the reddened mucous membrane of the mouth, small bubbles are visible, which are located in groups - a sign of a herpetic lesion.
- An increase in body temperature, weakness, swollen lymph nodes, and other manifestations of intoxication are also characteristic of acute herpes stomatitis.
- The child cries and refuses to eat.

For children older than one year
At this age, symptoms of stomatitis may include:
- Ulcerative painful lesions of the oral cavity (its mucous membrane) in the form of round whitish-gray aphthae.
- Bubble rashes on the oral mucosa.
- Slight fever, slight weakness.
- Enlarged lymph nodes and their soreness.
- appearance of gingivitis.
- Bad breath.

Causes
The disease can be caused by very different reasons - from viruses and "dirty hands" to severe immunodeficiencies. Read about what the famous pediatrician E. Komarovsky thinks about stomatitis in another article.
In infants
Fungi are the most common cause of stomatitis in infants. During the appearance of teeth, stomatitis may develop under the influence of bacterial flora, because the child pulls various objects into his mouth and injures the oral mucosa.
An infant older than 6 months can become infected by the mother or other adults with the herpes virus, causing him to develop acute stomatitis with blisters.

For children older than one year
The appearance of stomatitis in older children contributes to a violation of the rules of oral hygiene. The occurrence of stomatitis is associated with mucosal trauma, finger licking, allergens entering the child's body, the use of toothpastes with sodium lauryl sulfate, untreated caries, mouth breathing, acidic foods and other provoking factors. Also, often the defeat of the oral mucosa in a child is caused by viruses.
Types and forms
Stomatitis in children is of different types, some of which are more common (for example, aphthous and candidiasis), while others are less common.
aphthous

hand-foot-mouth syndrome
This type of stomatitis is manifested not only by the appearance of painful whitish sores in the mouth and fever, but also by the appearance of a rash on the feet and palms in the form of grayish blisters that hurt. The same bubbles can appear on the skin of the buttocks and in the genital area.
The disease is contagious and most often diagnosed in children under 10 years of age. It is caused by enteroviruses, which are transmitted through particles of mucus, feces and saliva from a sick person. Infection is possible through common dishes, a towel, hand contact, a pond.
The incubation period lasts about one week. The child becomes contagious a few days before the first manifestations of this syndrome and releases viruses up to 2 months from the onset of the disease.

The child's body temperature suddenly rises (it can reach 39-40 degrees), chills and weakness appear. Further, in the oral cavity (on the lips, cheeks, tongue), ulcerative lesions appear, which have uneven edges and a whitish tint. They are very painful and cause great discomfort to the child. At the same time, parents may notice a rash on the feet and palms, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, and sore throat in the child.
Usually such a disease lasts 7-10 days and ends with a complete recovery. In rare cases, complications affecting the heart and nervous system are possible. Repeatedly this syndrome is ill in very rare cases. Antiviral agents are not used in the treatment, but only eliminate unpleasant symptoms. With fever, the child is given an antipyretic, sores in the mouth are lubricated with an anesthetic gel. Bubbles on the skin of the feet and hands do not need to be treated with anything.
It is important that the child drinks enough during this form of stomatitis. Avoid eating acidic foods as they can make your mouth pain worse. The child can be given cold milk or ice cream.
About stomatitis in the tongue of a child, read another article.

Allergic and contact
Such forms of stomatitis are caused by exposure to chemicals and allergens.
Swelling of the tongue or lips may suggest that the cause of stomatitis may be an allergy. Also, the allergic nature of the lesion can be judged by all cases of stomatitis, if we analyze the circumstances under which they began. You need to look for a connection with food, visiting a dentist, using hygiene products.
Most often, such stomatitis is caused by flavors, preservatives and flavoring components of toothpastes, metal prostheses and fillings, sucking tablets and lozenges, sprays for the throat and mouth.

What disease can be a sign?
Although rare, stomatitis can be one of the symptoms of such serious pathologies as oral cancer, HIV, leukemia, celiac disease, diabetes mellitus, Crohn's disease, Stevens-Jones syndrome, heavy metal intoxication, Kawasaki disease and other pathologies. To exclude these diseases, with stomatitis it is important to show the child to the doctor.
When should you see a doctor?
A child with stomatitis must be examined by a doctor if:
- Simultaneously with the defeat of the mouth, the child developed blisters on the trunk, legs or skin of the hands.
- The body temperature of the child has risen and the state of health has deteriorated.
- The child also inflamed other mucous membranes, for example, the genitals and eyes.
- In addition to stomatitis, the child has headaches, a rash, itching, breathing problems and other adverse symptoms.
- The ulcer on the oral mucosa is very large - more than one centimeter in diameter.
- In the child's mouth, there are more than 7-10 mucosal lesions.
- Until the old sores are completely healed, new ones appear in the child.
- Stomatitis worries the child very often, appearing every month.
- The ulcer formed in the mouth does not heal for more than three weeks.

What to do if relapses are frequent?
If stomatitis appears in a child very often, you should:
- Visit the dentist and cure all teeth.
- Pay attention to oral hygiene - brush your teeth at least twice a day, rinse your mouth after meals, take your time brushing your teeth and use brushes with soft bristles.
- Stop using antiseptics, which treat the oral cavity.
- Avoid using toothpastes with sodium lauryl sulfate.
- Limit food that can injure the mucous membrane or cause irritation on it, for example, citrus fruits, crackers, spicy dishes, chips.
- Eliminate all foods that the child is allergic to.
- Take vitamin and mineral supplements regularly.

FAQ
First of all, one that does not hurt the gums during use. At the same time, the quality of oral hygiene depends more on whether the teeth are brushed correctly than on the shape or type of toothbrush. As for electric brushes, for uninformed people they are the preferred option; although you can brush your teeth with a simple (manual) brush. In addition, a toothbrush alone is often not enough - flosses (special dental floss) should be used to clean between the teeth.
Rinses are additional hygiene products that effectively clean the entire oral cavity from harmful bacteria. All these funds can be divided into two large groups - therapeutic and prophylactic and hygienic.
The latter include rinses that eliminate unpleasant odors and promote fresh breath.
As for therapeutic and prophylactic, these include rinses that have an anti-plaque / anti-inflammatory / anti-caries effect and help reduce the sensitivity of hard dental tissues. This is achieved due to the presence in the composition of various kinds of biologically active components. Therefore, the rinse must be selected for each individual on an individual basis, as well as toothpaste. And in view of the fact that the product is not washed off with water, it only consolidates the effect of the active components of the paste.
Such cleaning is completely safe for dental tissues and less injures the soft tissues of the oral cavity. The fact is that in dental clinics a special level of ultrasonic vibrations is selected, which affects the density of the stone, disrupts its structure and separates it from the enamel. In addition, in places where tissues are treated with an ultrasonic scaler (this is the name of the device for cleaning teeth), a special cavitation effect occurs (after all, oxygen molecules are released from water droplets, which enter the treatment zone and cool the tip of the instrument). The cell membranes of pathogenic microorganisms are torn by these molecules, causing the microbes to die.
It turns out that ultrasonic cleaning has a complex effect (provided that really high-quality equipment is used) both on the stone and on the microflora as a whole, cleaning it. And you can't say the same about mechanical cleaning. Moreover, ultrasonic cleaning is more pleasant for the patient and takes less time.
According to dentists, dental treatment should be carried out regardless of your position. Moreover, a pregnant woman is recommended to visit a dentist every one to two months, because, as you know, when carrying a baby, the teeth are significantly weakened, they suffer from a deficiency of phosphorus and calcium, and therefore the risk of caries or even tooth loss increases significantly. For the treatment of pregnant women, it is necessary to use harmless anesthesia. The most suitable course of treatment should be selected exclusively by a qualified dentist, who will also prescribe the required preparations that strengthen tooth enamel.
Treating wisdom teeth is quite difficult due to their anatomical structure. However, qualified specialists successfully treat them. Prosthetics of wisdom teeth is recommended when one (or several) neighboring teeth are missing or need to be removed (if you also remove a wisdom tooth, then there will simply be nothing to chew on). In addition, the removal of a wisdom tooth is undesirable if it is located in the correct place in the jaw, has its own antagonist tooth and takes part in the chewing process. You should also take into account the fact that poor-quality treatment can lead to the most serious complications.
Here, of course, much depends on the taste of the person. So, there are absolutely invisible systems attached to the inside of the teeth (known as lingual), and there are also transparent ones. But the most popular are still metal braces with colored metal / elastic ligatures. It's really trendy!
Let's start with the fact that it's just unattractive. If this is not enough for you, we give the following argument - the stone and plaque on the teeth often provoke bad breath. And that's not enough for you? In this case, we move on: if the tartar “grows”, this will inevitably lead to irritation and inflammation of the gums, that is, it will create favorable conditions for periodontitis (a disease in which periodontal pockets form, pus constantly flows out of them, and the teeth themselves become mobile). ). And this is a direct path to the loss of healthy teeth. Moreover, the number of harmful bacteria at the same time increases, due to which there is an increased cariousness of the teeth.
The service life of an accustomed implant will be tens of years. According to statistics, at least 90 percent of implants function perfectly 10 years after installation, while the service life is on average 40 years. Tellingly, this period will depend both on the design of the product and on how carefully the patient takes care of it. That is why it is imperative to use an irrigator during cleaning. In addition, it is necessary to visit the dentist at least once a year. All these measures will significantly reduce the risk of implant loss.
Removal of a tooth cyst can be performed by a therapeutic or surgical method. In the second case, we are talking about the extraction of a tooth with further cleaning of the gums. In addition, there are those modern methods that allow you to save the tooth. This is, first of all, cystectomy - a rather complicated operation, which consists in removing the cyst and the affected root tip. Another method is hemisection, in which the root and a fragment of the tooth above it are removed, after which it (part) is restored with a crown.
As for the therapeutic treatment, it consists in cleaning the cyst through the root canal. It is also a difficult option, especially not always effective. Which method to choose? This will be decided by the doctor together with the patient.
In the first case, professional systems based on carbamide peroxide or hydrogen peroxide are used to change the color of teeth. Obviously, it is better to give preference to professional bleaching.
Contrary to popular belief, stomatitis itself in children is not a complication of a childhood cold, although it most often occurs against the background. The second common misconception about this disease erroneously claims that a pediatric dentist should be involved in the treatment of stomatitis in a child. Both of these are incorrect. Why stomatitis actually occurs in children, as well as who and how should treat it - let's figure it out!
Stomatitis delivers to children not only constant discomfort, but also severe aching pain.
View gallery 1 of 1
What is stomatitis and where to look for it in children?
Despite the fact that stomatitis in children often occurs as a result of SARS, there is no direct connection between these diseases. The point is that while the child is sick with a cold, his respiratory tract (including also the oral cavity) dries up significantly. Saliva is almost not secreted, local immunity in the oral cavity is greatly weakened.
As a result, the mucous membranes of the mouth are left without the necessary protection, and when viruses or bacteria “unfriendly” to the body get on them, inflammation occurs. It is precisely this inflammatory process on the mucous membranes of the mouth that is usually called "stomatitis". Unfortunately, the development of stomatitis in children gives children considerable pain.
Often, children behave extremely restlessly, cry all the time, refuse to eat, drink, and cannot sleep peacefully for a long time. In addition, even a mild inflammatory process in the oral cavity with stomatitis in children.
What kind of stomatitis does your child have: herpetic, aphthous or angular
There are many options for stomatitis - there is no point in listing them all. It is enough for parents to know that in children, in the vast majority of cases, one of the three most common types of stomatitis occurs - aphthous, herpetic and angular.
Aphthous stomatitis in children. Aphtha is a special medical term, behind which, as a rule, a specific designation is hidden: "a small area of \u200b\u200bthe mucous membrane on which there are damages." Most often, with aphthous stomatitis in children, foci of inflammation look like small round sores, covered with a yellowish or grayish coating and surrounded by a bright red rim.
Herpetic stomatitis in children. Herpetic stomatitis is a contagious disease that can affect a child at any age, but most often occurs in children 1-3 years old. Children who are in contact with each other (those who play with the same toys and often take them into their mouths, use the same dishes, etc.) easily transmit herpetic stomatitis to each other. The causative agent of herpetic stomatitis is one of the variants of the herpes virus. Most other types of stomatitis (including aphthous) are not contagious and are not transmitted from one child to another.
Angular stomatitis in a child. This type of stomatitis is well known to everyone under a more “simple” household name - “zaeds”. In medical reference books, it is listed as "angular" stomatitis, and is manifested by severe irritation of the skin in the corners of the mouth. Over time, cracks appear there. Most often, angular stomatitis occurs due to an acute shortage of iron in the body.
Causes of stomatitis in children
Stomatitis in the mouth of a child can be caused by a number of factors. A child can bite the inner surface of the cheek in a dream (or the baby simply has a jagged tooth) - and please, a place of irritation has appeared in the mouth. Also, stomatitis can occur due to a burn with hot food. Viral stomatitis in most cases occurs due to overdrying of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, against which the pathological activity of viruses increases dramatically.
The cause of herpetic stomatitis in children is the activity of the herpes virus of the first type (by the way, do not confuse stomatitis with genital herpes, which is caused by the activity of the herpes virus of the second type, as well as with any sexually transmitted diseases - there are no similarities here).
The exact causes of other types of aphthous stomatitis (not herpetic) have not yet been established, although several main factors are under consideration. One of the factors is the genetic predisposition to the development of ulcers, the other is the relationship of the disease with disorders in the immune system. In addition, stomatitis can be caused by emotional stress; nutritional deficiencies, iron deficiency, lack of vitamin B12. Sometimes stomatitis occurs as a result of a food allergy or viral infection.
Stomatitis in the mouth in a child: symptoms
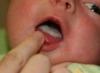
The main (and common for most variants of the disease) symptoms of stomatitis in children are visible to the naked eye when examining the oral cavity. Ask the baby to open his mouth and slightly pull his lower lip - most often this is where the aphthae-ulcers are located.
The size, foci, and color of ulcers can vary greatly. For parents, any heterogeneity in the child's mouth should be a signal of concern. In other words: normally, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity is pink, moisturized, quite smooth and the same in all areas. If somewhere you notice swelling, redness, "pimple", or even just irritation, etc. - this is already a reason to ask your attending pediatrician to examine the child's mouth for stomatitis.
In addition to a visual examination of the child's oral cavity, his behavior can also "hint" at stomatitis. Since the formation of ulcers causes real pain and discomfort in the baby, his behavior also changes dramatically - children become whiny and irritable, sleep poorly and refuse to eat.
In the case of herpetic stomatitis In addition to these general symptoms, special ones will also be added:
- Aphthae in the mouth appear almost simultaneously - that is, immediately in several places, approximately the same size.
- The disease is undulating: first, the mouth is covered with painful sores, which is accompanied by a sharp increase in temperature, then the disease seems to “freeze” (the child may cheer up and stop complaining of pain; the temperature stabilizes), and after a few days, a relapse occurs: new sores, again an increase temperature and pain.
- The gums swell and are observed.
To the characteristic symptoms of aphthous stomatitis in children include:
- A day or two before the appearance of afts (ulcers) and an increase in temperature, small bubbles pour out on the tongue, which gradually begin to cause a burning sensation. Doctors usually call this symptom of aphthous stomatitis "geographic tongue".
- Often, along with the bubbles, a whitish coating appears on the tongue.
A characteristic whitish coating on the tongue is often a symptom of stomatitis in children.
The number of ulcers in the oral cavity with aphthous stomatitis is much less than with herpetic stomatitis - most often one or two, sometimes up to five or six. Whereas with herpetic stomatitis in children, the entire mouth can be “sprinkled” from the inside.
In addition, with any acute stomatitis (not only with aphthous, but also with herpes, and with others), the lymph nodes under the lower jaw often increase and become painful.
How to treat stomatitis in children
Being a smart parent You should contact your doctor (pediatrician) if you find that:
- The child is unable to drink and swallow food.
- The child has a high temperature.
- The child is too fussy, it is impossible to calm him down.
- The child sleeps restlessly at night, or does not sleep at all.
- The baby's tongue appeared blisters and a light white coating.
Treatment of stomatitis in children directly depends on the causes that caused it. Common to all types of stomatitis in children is the following treatment strategy:
- A sparing diet with the exclusion of any solid foods that can “disturb” aphthae in the oral cavity and exacerbate inflammation. Also, spicy and sour foods should be removed from the diet, and food should not be too hot.
- Thorough oral hygiene: gentle brushing of teeth and tongue, as well as daily rinsing with antiseptic agents.
- If the child's temperature rises above 38.5 ° C, he should be given antipyretic medicine.
With a sparing diet and proper oral hygiene, aphthae (sores) completely disappear 10-15 days after their appearance with any type of stomatitis.
For rinsing the mouth during the day, you can use solutions of antiseptics - chlorhexidine, furacilin, etc., as well as decoctions of herbs - chamomile, calendula and others. The attending physician will tell you how to properly prepare the solution, and also prescribe a rinsing regimen (it varies depending on the age of the child and the severity of his illness). In addition, if the ulcers are large and so painful that the child behaves too hysterically, aphthae can be treated from time to time with antiseptic aerosols.
However, remember that with stomatitis in children, aerosols should never be used for children under one year old. Pharmacy gels, which are usually used to relieve itching, will help relieve pain in these crumbs.
Children's stomatitis can be aggravated by the pointed edges of the teeth or braces in the mouth - these problems are best solved in the office of a pediatric dentist.
Additional measures for the treatment of stomatitis in children
In addition to general methods of therapy against stomatitis in children, of course, there are special treatment measures that correspond to each specific type of this disease. For instance:
- If the diagnosis sounds like “herpetic stomatitis in a child”, the doctor will definitely prescribe a drug that suppresses the activity of the herpes virus (the main active ingredient of which is acyclovir).
- If the stomatitis is angular (jamming) - then for sure the child will be prescribed drugs,.
What parents always miss: alas, iron deficiency in the body cannot be replenished with food - it will take too much time (not a single year). Iron-containing foods - beans, apples, meat or nuts - all of them are only able to maintain the level of iron that the body already has. Only special medications can raise the level of iron content.
- If aphthous stomatitis in the child's mouth does not go away for more than 15 days, immediately consult a doctor again.
Alas, there is no special prevention against stomatitis in children - the cause may be a banal injury to the oral mucosa caused by a solid piece of food or a children's toy. However, if the baby has strong, stable immunity, the chances that the disease will develop are significantly less.
Have you found a sore in your child's mouth and don't know what to do? In this article, you will learn what types of stomatitis are, how they differ, their symptoms and causes. And also what medicines and folk remedies can treat stomatitis at home.
If the child is whiny, has poor sleep and appetite, may even have a temperature and complains of pain in the mouth, parents should suspect stomatitis. Look into the baby's mouth, most likely you will find sores or redness there. Do not treat stomatitis yourself, because. for effective treatment, you need to find out the cause of the disease, it can be caused by both viruses and fungi or bacteria.
What are the types of stomatitis in a child?
There are several main types of stomatitis that most often occur in children:
- candidal stomatitis, most often occurs in children under 3 years of age
- aphthous stomatitis, this allergic disease often occurs in schoolchildren
- herpetic (viral) stomatitis, usually observed in children from one to three
- angular stomatitis, in a simple way - “zaeds”
- bacterial stomatitis, occurs when the oral mucosa is injured and hygiene is neglected (unwashed foods, hands), often occurs in young children who put everything in their mouths
Stomatitis often occurs in babies, because. their delicate oral mucosa is easily injured, and their immunity is not yet working properly and simply cannot cope with all infections. The saliva of young children does not contain the necessary amount of enzymes that act as antiseptics.


Stomatitis of any kind can occur in different forms, both mild and severe, may be chronic or have relapses.
Herpetic stomatitis in children
This form most often occurs in both children and adults. This happens because almost all people become infected with the Herpes virus, but whether an adult or a child will get sick depends on immunity.
This virus is dangerous because it is always present in the body, it can be in a latent state or become a chronic disease with constant relapses.
If the child's body is faced with this virus, it will actively fight, therefore, with herpetic stomatitis, the child has a high temperature and there are signs of intoxication of the body.


Features of herpetic stomatitis:
- redness appears on the mucosa at the beginning of the disease, then vesicles appear, when the bubbles burst, ulcers or cracks appear
after healing of ulcers, a marble pattern can be seen on the mucosa
the child becomes irritable, does not want to eat, because. ulcers burn and itch - this type of stomatitis can be confused with SARS, because. the same symptoms are observed: the temperature first rises to 38 ° C, the lymph nodes increase, then after the appearance of ulcers the temperature rises to 39 ° C and is often poorly controlled by drugs, nausea and vomiting may occur, a headache and chills appear
- in the acute period of the course of the disease, up to 20 ulcers can be counted, which can be not only in the mouth, but also on the nose and lips, while the gums are inflamed and dry mouth is felt
- if the disease is easily tolerated, there are usually up to 6 ulcers, the temperature does not rise above 38 ° C, it is easily confused and the child recovers quite quickly
Candidiasis or fungal stomatitis (thrush)
Candidiasis stomatitis usually appears in infants in the form of thrush, which is easy to recognize by the characteristic white coating on the tongue and even lips.


Features of fungal stomatitis:
- the disease usually resolves without fever
- sores may be with a white or gray coating, reminiscent of cottage cheese
- the wounds are very painful, I can burn, itch, there is a feeling of dryness, so the child is naughty, he has restless sleep and poor appetite
- sores often appear on the gums, the inner surface of the lips and cheeks, as well as on the tongue
- lesions have a white coating that turns into a homogeneous film
Aphthous stomatitis in children
It is believed that aphthous stomatitis occurs due to improper functioning of the digestive system, other doctors believe that it occurs due to allergic reactions that lead to injury to the mucosa. Due to the ambiguity of the causes of this type of stomatitis, it is quite difficult to treat it.


Features of aphthous stomatitis:
- ulcers are similar to mucosal lesions as in herpetic stomatitis, redness, itching are also observed, the temperature may rise
- then there are aphthae instead of bubbles - these are white sores, around which there is redness, and they hurt very much, the shape of the aphthae is round and smooth edges
- further, a cloudy film appears at the sores
- if the infection was reintroduced after the ulcer broke through, the course of the disease worsens, the body temperature of the child may increase
Angular stomatitis in children
Seizures, wet cracks in the corners of the mouth, most often appear due to a lack of iron in the children's body. Also, angular stomatitis is caused by streptococci or yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. These fungi can be found on the mucous surface of the child and cause disease when the body's immunity is reduced and vitamins are not adequately received.


Features of angular stomatitis:
- cracks in the corners of the mouth, depending on the causes, can be without a crust, lacquer red and with a grayish coating (fungal) and with a purulent crust, if it is torn off, the wound will bleed (streptococcal)
- fungal stomatitis often turns into a chronic disease
- angular stomatitis can occur due to malocclusion
- poor hygiene also provokes this disease, as well as the presence of caries in the mouth
This type of stomatitis sometimes worries the child very much, because. in the absence of treatment or improper treatment, the child's condition worsens, it becomes painful to open his mouth to say something or eat.
Bacterial stomatitis in children

 Bacterial stomatitis
Bacterial stomatitis This type of stomatitis is caused by bacteria that live in the human body. With a decrease in immunity due to the presence of diseases of the teeth, as well as the tonsils and nasopharynx, the bacteria become active. However, stomatitis does not occur if the mucous membranes are not injured, but with the slightest damage, the bacteria will immediately penetrate there.
Features of bacterial stomatitis:
- the disease begins with pain during eating, especially acidic and spicy foods
- then the mucous surface of the mouth turns red, ulcers appear, they cause a burning sensation, itching, the mucous membrane swells, there is an unpleasant odor
- it becomes painful to brush your teeth, because. swollen gums, their surface is loose, bleeding
- the infection can go further down the nasopharynx, in such cases, the child also has tonsillitis
Stomatitis in children: symptoms
The main symptom of the presence of stomatitis in a child is sores in the mouth, most often they are located behind the lower lip and you can see them by bending it back and looking inside.
Ulcers are different in structure, from fairly well-marked pimples and redness, to slight irritation. Therefore, parents need to be vigilant and carefully examine the entire oral cavity - the mucous membrane normally has a uniform pink color and a smooth structure.
A secondary symptom in children is changes in their behavior: they begin to be mischievous, naughty, eat and sleep poorly, because. sores are quite painful and disturb babies.
Another common symptom of stomatitis is an increase in the lymph nodes that are located under the jaw. In addition to being enlarged, they are also painful.
Also, if stomatitis herpetic The child has the following symptoms:
- sores occur at the same time in different places, and they are almost the same size
- a second wave of the disease is possible: first ulcers appear and the temperature rises, then everything goes away, but after a few days it starts again
an unpleasant odor comes from the mouth - slightly swollen gums
If stomatitis aphthous children develop the following symptoms:
- a couple of days before the main symptoms, small lesions of the tongue appear, which cause a burning sensation, this symptom is called "geographic tongue"
- often a white coating appears on the tongue of the child

 "Geographic language"
"Geographic language" Stomatitis in children under one year old
The children's body is not yet strong enough to repel the attacks of various viruses, bacteria and fungi, so stomatitis often occurs in babies. Breastfed children under one year of age partially receive immunity from mother's milk, but this is not always enough to avoid getting sick.
In infants, fungal stomatitis most often occurs, which is not at all difficult to recognize. White plaque on the lips, palate, inner surface of the lips and cheeks, on the tongue is a visiting card of stomatitis caused by a fungus. Also, quite often, babies get sick with a viral type of this disease.


It is important for children from birth to monitor personal hygiene and oral hygiene, temper the child's body and protect it from infections.
How to treat stomatitis in children under one year old?
- First you need to determine viral or fungal stomatitis, because. treatment will be different.
- Keep it clean: wash the toys that the child plays with and licks well, it is better, of course, to pour boiling water over them, as well as baby bottles and nipples
- Give food that is neutral in taste, not sour, not salty, without spices, so that it does not irritate the sores even more
- If stomatitis is thrush (thrush), stop giving your child dairy products for a while
- After each meal, you need to treat the sores with an antiseptic, for example, soda solution or furacilin solution
- Give medication as prescribed by the doctor. Often doctors prescribe Holisal gel, it also contains an anesthetic that will remove pain from the baby.
- In acute forms of stomatitis, you may have to undergo disinfecting physiotherapy


Parents should understand the condition of the crumbs and be patient with his whims. Their condition is further complicated by the fact that small children seek solace in sucking, and often all diseases are carried out under the mother's breast, but in this case, sucking will cause pain. Therefore, you need to start treatment as soon as possible.
How to treat stomatitis in a child 1 and 2 years old?
Children at this age are small explorers and very active, so viral stomatitis often occurs.
Viral stomatitis is dangerous because it spreads quickly. In no case do not take the child to the playground or to the nursery, at this age children often exchange saliva through their hands and toys, so you risk infecting all the children with whom your baby will come into contact.


Take all preventive measures to avoid contracting viral stomatitis:
- often do wet cleaning in the house, wash toys
- make sure your child is washing their hands well and often
- sterilize bottles, nipples and other personal belongings of the child
- the child's personal belongings should be his only, do not lick his spoon, and do not try tea from his cup - you can be a carrier
- do not walk with children who are now bleating with stomatitis
- boost your baby's immunity
- make sure the baby doesn't freeze
How to treat stomatitis in children in the mouth? Medicines and preparations for stomatitis for children
At herpetic stomatitis, the basis of treatment will be a drug that reduces the activity of the herpes virus, for example, Acyclovir or Viferon. These drugs have antiviral properties, but their use is advisable in the first 2-3 days of the onset of the disease, before the bubbles burst.


For rinsing, you need to use solutions that are active against the Herpes virus, for example, Miramistin. You need to rinse 3-4 times a day. However, small children do not know how to rinse their mouths, so soak a cotton swab in the solution and wipe the mucous surfaces of the child's mouth with it.


You can rinse the baby's mouth as follows: draw the medicine into a small pear, tilt the child upside down so that he does not choke, and inject the solution into his mouth.
At aphthous stomatitis, the duration of the disease should not exceed two weeks, otherwise consult a doctor immediately. Since there are several causes of aphthous stomatitis, the treatment is different.
The first step is to exclude foods that are possible allergies, and foods that can aggravate the disease (sour, spicy, rough foods).
Antihistamines such as Suprastin or Claritin are prescribed. The oral cavity is treated with Miramistin in the initial and middle periods of the disease, as well as spot treatment with Holisal aft gel.

 Gel Holisal from stomatitis
Gel Holisal from stomatitis At the end of treatment, epithelializing agents are used to treat the damaged mucosa. Physiotherapy with ultraviolet rays is also often used.
At angular stomatitis, the doctor will probably prescribe iron supplements to the child.
In no case do not hope to fill the iron deficiency with foods, they can only maintain the required level, but if it is not enough, you must definitely take iron supplements, and do not ignore the doctor's prescription.
Folk remedies for stomatitis in children. Treatment of stomatitis at home
Quite often, the treatment of stomatitis at home with folk remedies gives positive results.
Mouth treatment
To wipe the mucous surface of the child's mouth, you can prepare a soda solution, for this, dilute 1 teaspoon of baking soda in a glass of boiled water. Wrap a bandage around your finger and, dipping in a soda solution, lubricate the damaged areas. At the same time, gauze will remove plaque, and soda will disinfect the wounds.

 Mouthwash for stomatitis
Mouthwash for stomatitis In the same way, treat the damaged areas with ordinary brilliant green, it also helps well with stomatitis.
Herbal infusions
A good antiseptic is an infusion of chamomile. Prepare it by pouring 1 teaspoon of dried flowers into a glass of boiling water, leave to steep and strain when it has cooled. Rinse the decoction of the mouth several times a day.
Strongly brewed green tea is good, but for kids it is better to make a decoction of calendula.
You can also make rose syrup for children: pour washed tea rose petals with sugar in a ratio of 1: 2 and leave overnight, then heat in a water bath until the sugar dissolves completely. You need to treat your mouth with this syrup after eating, the child will gladly give you this delicious procedure.


You can also brew oak bark, yarrow, burdock, sage, or a mixture of these herbs. Rinse your mouth with decoctions after each meal.
You can also use aloe at home. Give the child a well-washed aloe leaf and ask him to chew, but if the baby does not want to, you can grind it and apply the resulting slurry to the affected area. So that the child does not harm, you can add one spoon of honey.
Product use
If the child does not have allergies, when the sores have just begun to appear, lubricate them with honey.
Another folk remedy is raw potatoes. Apply a gruel of grated potatoes to the affected areas and hold for about 5 minutes at least 2 times a day, this treatment should be carried out for about a week.


If you are not allergic to egg white, you can use it to eliminate the symptoms of stomatitis. To do this, mix the protein of one egg with a glass of boiled water and rinse your mouth with this mixture about 4 times a day. At the same time, the wounds are wrapped around, so that they heal faster.
natural oils
To heal the wounds faster, you can use various oils, such as peach, flax or rosehip oil. After treating your mouth with antiseptics, lubricate them with oil. Such treatment should be carried out at least 4 times a day, and do not skip the procedures, regularity is important here.


It should be noted that it is not necessary to treat a child for stomatitis on their own. Be sure to consult with your doctor whether such treatment will be effective in this particular case and whether it will help to cure your child of the type of stomatitis that he fell ill with.
VIDEO: Stomatitis in a child. How to recognize and how to treat - School of Dr. Komarovsky
Stomatitis in children is an irritation of the oral mucosa that occurs in children from the age of three years and babies up to a year. The causes of stomatitis are transferred infectious diseases, severe colds and SARS. But it is worth noting that the disease is not a complication of these processes, but manifests itself as a result of a decrease in immunity after their transfer. This happens because during a viral illness, the oral cavity dries up due to a slight flow of saliva, which in ordinary life protects the mouth from the effects of pathogenic microorganisms.
Children's stomatitis is often accompanied by an increase in body temperature, which parents mistakenly treat at home with antibiotics. Such drugs only worsen the situation and further reduce the immunity of babies. The disease is expressed by the appearance of small pimples, ulcers on the oral mucosa, as well as its swelling, all this is accompanied by a significant increase in body temperature (the child experiences severe pain).
It is possible to diagnose and determine the causes of stomatitis in children only by a pediatric dentist, after a complete examination of the mouth. Under no circumstances should stomatitis in children be treated at home. Parents should only examine the daily oral cavity of the baby from one year of life to three years.
Etiology
Doctors identify many causes of such a disease in children, but the most predominant of them are:
- genetic predisposition;
- burns of the oral mucosa from very hot food or drinks;
- unintentional biting by the baby of the inner surface of the cheeks or tongue;
- getting into the oral cavity of a fungal infection in any way;
- viral;
- non-observance of hand hygiene after visiting the toilet or walking on the street. The kid puts dirty hands in his mouth, which can serve as the beginning of the development of the inflammatory process;
- children's habit of pulling everything that surrounds them into their mouths;
- mouth injury from a fall;
- scratches due to a foreign object;
- teething is the most common cause of stomatitis in infants;
- transferred viral diseases -,;
- infections unusual for a child's body -,;
- inept brushing of teeth;
- allergic pathogens;
- dental braces;
- premature birth;
- vitamin deficiency;
- some medications.
The oral mucosa of young children, especially those under one year of age, is so thin that any exposure can cause stomatitis.
Varieties
According to the forms of flow, stomatitis happens:
- sharp - appeared for the first time in my life;
- chronic - recurring symptoms.
Depending on the causes:
- herpetic - the herpes virus enters the oral cavity through foreign objects;
- angular - the child himself is the carrier of the infection, which means that he gets sick through dirty hands;
- aphthous stomatitis in children - appears due to allergic effects;
- viral - occurs due to the action of bacteria. The rash looks like small transparent bubbles on the tongue, cheeks, lips and larynx.
By age group:
- candidiasis - appears in babies from the moment of birth to three years. Expressed as small white dots on the gums, cheeks and tongue;
- allergic - typical for children of primary preschool age;
- bacterial - can be expressed in children of any age, but not older than seven years.
By the presence of scars after healing:
- with scars;
- without them;
- temporary scars - disappear a few weeks after recovery.
According to the severity of symptoms:
- mild - without characteristic signs of the disease;
- medium - there are a lot of rashes, the child's condition worsens every day;
- severe - multiple rashes, body temperature rises significantly.
Symptoms
Despite the wide variety of types of childhood stomatitis, they all have similar symptoms, including:
- stale and unpleasant smell from the mouth;
- increased separation of saliva;
- gluing lips;
- change in the color of the oral mucosa - it acquires a bright red or burgundy hue;
- intoxication of the body;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- swelling of the gums;
- yellowish coating on the tongue and gums;
- an increase in the number of ulcers in the mouth (every day).
The manifestation of stomatitis in infants has its own characteristics:
- baby crying while breastfeeding
- refuses to breastfeed;
- appetite decreases;
- body temperature rises;
- the child is constantly in anxiety;
- sleep disturbance.
Diagnostics
Only a doctor can distinguish stomatitis from other diseases of the oral cavity. It is strictly forbidden for parents to carry out any manipulations in the child's oral cavity at home (especially for babies under one year old). If these symptoms appear, you should immediately go to the doctor.
To determine a clearer picture of the course of the disease, the doctor may additionally prescribe studies:
- and . Sometimes a fecal sampling is carried out - to identify particles of worms in the patient's body;
- laboratory examination of a scraping or smear from the oral cavity;
- cytological diagnostics;
- virological;
- bacteriological;
- immunological.
These activities are carried out to accurately identify the causative agents of the symptoms of the disease.
Treatment
Adults often wonder how to treat stomatitis in children on their own, without going to the clinic. It is strictly forbidden to treat stomatitis in a child at home. Treatment can only be prescribed by a pediatric dentist together with a therapist.
Treatment of stomatitis is aimed at:
- elimination of the intensity of the manifestation of symptoms with the help of antiviral drugs and ointments;
- rinsing the mouth with antiseptics every time after eating;
- painkillers;
- healing of sores with the use of special toothpastes and ointments.
- the use of special sprays with active substances. For children under one year of age, their use is not recommended.
To help relieve pain:
- sea buckthorn oil;
- ointments with rosehip extract;
- anesthetic gels.
If there is a repeated expression of stomatitis in infants, an urgent need to consult an immunologist.
Treatment of stomatitis in children, especially those who have not reached the age of one, should be carried out under the full supervision of a physician, and under no circumstances (even if symptoms are mild) should stomatitis therapy be carried out at home.
Prevention
Prevention of childhood stomatitis should be carried out by parents - especially carefully for children who are not yet a year old. Parents are required to:
- protect children from any injuries by securing the home environment in which the child lives;
- timely treat viral and infectious diseases of the baby;
- daily examine the oral mucosa of the child (especially closely the first three years of his life);
- disinfect nipples, bottles and nipples before feeding the baby;
- monitor the baby's hand hygiene;
- after the child's teeth have erupted, regularly show it to the pediatric dentist;
- brush your children's teeth on your own or always be present at this process, use special pastes intended only for children;
- provide the child with a balanced diet enriched with vitamins, calcium and other minerals;
- never treat a child for any diseases on their own, at home.
Is everything correct in the article from a medical point of view?
Answer only if you have proven medical knowledge
Diseases with similar symptoms:
Aphthous stomatitis is a type of ordinary inflammation of the oral mucosa, accompanied by the appearance of aphthae, i.e. small white ulcers with a red border, which are in the shape of a circle or oval (may occur singly or appear in large numbers). The main symptoms of the disease are - unpleasant sensations in the form of pain and burning, aggravated during meals. Neoplasms heal in about ten days, leaving no traces behind, only some types of ailment can provoke scars.